What is EMI Electromagnetic Interference
Background
Electromagnetic interference (EMI) is broadly defined as any electrical or magnetic interference that degrades or interferes with the signal integrity or the components and functions of electronic equipment. Electromagnetic interference, including radio frequency interference, generally falls into two broad categories. Narrowband emissions are usually man-made and confined to a small region of the radio spectrum. Hum from power lines is a good example of narrowband emissions. They are continuous or sporadic. Broadband radiation can be man-made or natural. They tend to affect broad regions of the electromagnetic spectrum. They are his one-off events that are random, sporadic, or continuous. Everything from lightning strikes to computers produces broadband radiation.
EMI source
The electromagnetic interference that EMI filters deal with can come in many different ways. Inside electrical equipment, interference can occur due to impedance, reverse currents in interconnecting wires. It can also be caused by voltage changes in conductors. EMI is generated externally by space energy such as solar flares, power or telephone lines, appliances, and power lines. Most of the EMI is generated along power lines and transmitted to equipment. EMI filters are devices or internal modules designed to reduce or eliminate these types of interference.
EMI filter
Without delving into the rigorous science, most electromagnetic interference is in the high frequency range. This means that when measuring a signal such as a sine wave, the periods will be very close. EMI filters have two components, a capacitor and an inductor, that work together to suppress these signals. Capacitors suppress direct currents and pass alternating currents through which large amounts of electromagnetic interference are brought into the device. An inductor is essentially a tiny electromagnet that retains energy in a magnetic field when current passes through it, reducing the overall voltage. Capacitors used in EMI filters, called shunt capacitors, keep high frequency currents within a certain range away from a circuit or component. A shunt capacitor feeds a high frequency current/interference to an inductor placed in series. As current passes through each inductor, the overall strength or voltage drops. Ideally, inductors reduce interference to zero. This is also called a short to ground. EMI filters are used in a wide variety of applications. They are found in laboratory equipment, radio equipment, computers, medical equipment, and military equipment.
Learn about our EMI/EMC filtering solutions
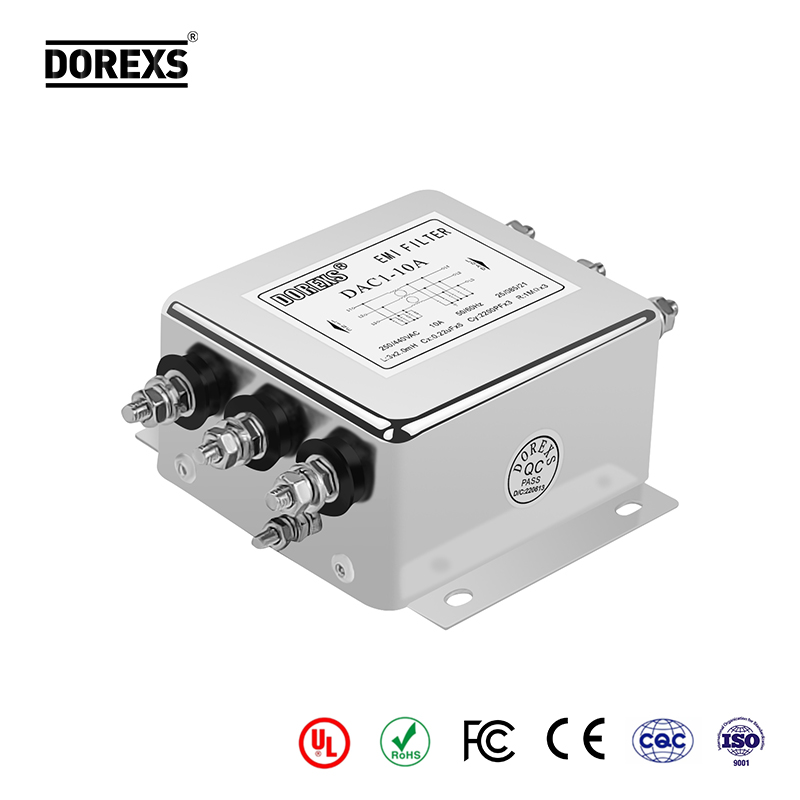

Capacitors suppress direct currents and pass alternating currents through which large amounts of electromagnetic interference are brought into the device. An inductor is essentially a small electromagnetic device that retains energy in a magnetic field when current is passed through it, causing an overall voltage drop. Capacitors used in EMI filters, called shunt capacitors, keep high frequency currents within a certain range away from a circuit or component. A shunt capacitor feeds a high frequency current/interference to an inductor placed in series. As current passes through each inductor, the overall strength or voltage drops. Ideally, inductors reduce interference to zero. This is also called a short to ground. EMI filters are used in a wide variety of applications.
Learn more about DOREXS EMI filters here.
Post time: Dec-20-2022